
Understanding Adult Ear Infections

An ear infection occurs when a bacterial or viral infection affects the ear, leading to inflammation and fluid buildup. Adult ear infections can be categorized into three main types:
- Outer Ear Infections (Otitis Externa): Also known as “swimmer’s ear,” this occurs when the outer ear canal becomes infected, often due to water remaining in the ear after swimming or bathing.
- Middle Ear Infections (Otitis Media): This type occurs when fluid builds up behind the eardrum, often due to colds, allergies, or sinus infections.
- Inner Ear Infections (Labyrinthitis): These infections are less common but can affect balance and hearing, as the inner ear plays a crucial role in both.
Common Signs of Adult Ear Infections
The symptoms of an ear infection can vary depending on the type and severity of the infection. Here are some key signs to watch for:
Outer Ear Infection Symptoms:
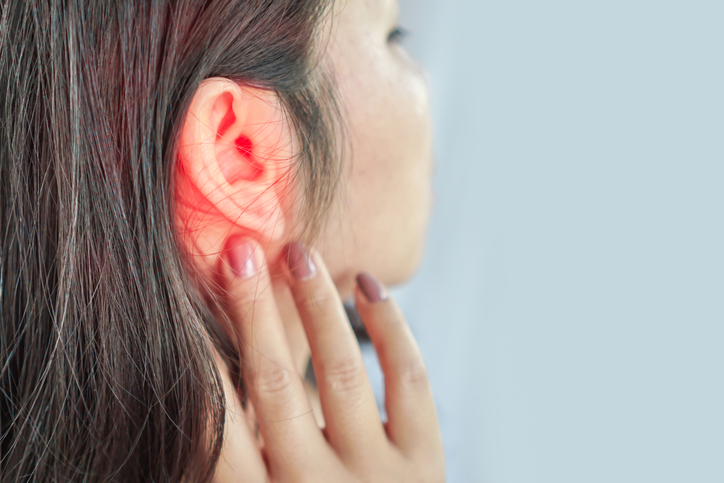
- Redness and swelling of the outer ear
- Pain or tenderness when touching the ear or moving the jaw
- Itchiness in the ear canal
- Discharge of fluid, often with a foul odor
- Partial hearing loss or a feeling of fullness in the ear
Middle Ear Infection Symptoms:
- Ear pain, often sharp or throbbing
- Pressure or fullness in the ear
- Reduced hearing
- Fluid drainage, which may be clear, yellow, or bloody
- Fever and fatigue
Inner Ear Infection Symptoms:
- Dizziness or vertigo
- Nausea and vomiting
- Ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Hearing loss
- Difficulty with balance or coordination
If you experience severe symptoms, such as high fever, intense pain, or sudden hearing loss, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of ear infections in adults:
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Colds, flu, and sinus infections can lead to fluid buildup and inflammation in the middle ear.
- Allergies: Seasonal or environmental allergies may cause nasal congestion and block the Eustachian tubes.
- Water Exposure: Swimming or prolonged exposure to moisture can increase the risk of outer ear infections.
- Earwax Buildup: Excess earwax can trap bacteria and lead to infections.
- Smoking: Tobacco smoke irritates the respiratory tract and can impair the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Weakened Immune System: Chronic illnesses or conditions that compromise immunity make individuals more susceptible to infections.
Prevention Tips for Adult Ear Infections

While it’s not always possible to prevent ear infections, adopting certain habits and practices can significantly reduce your risk:
1. Maintain Proper Ear Hygiene
- Avoid inserting objects, such as cotton swabs, into your ear canal, as this can push earwax deeper or cause injury.
- Clean the outer ear gently with a damp cloth if needed.
2. Keep Ears Dry
- After swimming or bathing, dry your ears thoroughly by tilting your head to each side to allow water to drain out.
- Use earplugs or a swim cap to keep water out while swimming.
- Consider using over-the-counter ear-drying drops if you’re prone to swimmer’s ear.
3. Manage Allergies and Congestion
- Use antihistamines or decongestants during allergy seasons to minimize nasal congestion.
- Avoid known allergens that trigger your symptoms.
4. Quit Smoking
- Smoking can damage the cilia (tiny hair-like structures) in your respiratory tract and hinder the drainage of fluid from your ears.
- Seek support or programs to help you quit smoking if needed.
5. Strengthen Your Immune System
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins to support overall health.
- Stay hydrated and get enough sleep.
- Exercise regularly to boost your immune system.
6. Address Underlying Health Issues
- Treat chronic conditions, such as diabetes or allergies, that may increase your risk of infections.
- Visit your healthcare provider regularly for check-ups.
7. Protect Your Ears During Travel
- Use earplugs or chew gum during flights to help equalize pressure in the ears.
- Avoid flying with a severe cold or sinus infection, as changes in air pressure can worsen ear discomfort.
8. Avoid Sharing Personal Items
- Do not share earbuds, headphones, or towels, as these can spread bacteria and viruses.
When to See a Doctor
While many mild ear infections resolve on their own, there are times when medical intervention is necessary. See a doctor if:
- Symptoms persist for more than a few days or worsen over time.
- You experience severe pain, high fever, or drainage from the ear.
- Hearing loss or balance issues develop.
- You have a history of recurrent ear infections.
A healthcare provider may recommend treatments such as:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Antifungal medications for fungal infections
- Pain relievers to manage discomfort
- Ear drops to reduce inflammation and promote healing
Long-Term Care and Monitoring
Recurrent or chronic ear infections may require additional care:
- Hearing Tests: Regular tests can monitor any long-term effects on your hearing.
- Surgical Interventions: In severe cases, procedures such as ear tube placement or removal of adenoids may be necessary.
- Therapy for Underlying Conditions: Addressing contributing factors like allergies or sinus issues can reduce recurrence.
Conclusion
Adult ear infections, though often less common than in children, can still cause significant discomfort and complications if untreated. Recognizing the signs of an ear infection and adopting preventive measures can help you maintain healthy ears. By keeping your ears dry, managing allergies, and strengthening your immune system, you can reduce your risk of infections. If symptoms persist or worsen, don’t hesitate to seek professional medical care. Your ears are vital to your overall well-being—protect them with proactive care and attention.


